|
|
 |
 |
| |
The manufacturing execution system (MES) market surpassed the $1 billion mark last year for the first time in world wide sales but this does not represents the potential of the market. As most of the manufacturing companies need visibility to accurate workflow information in order to optimize management control over the resources needed to deliver against sales demand, more companies are expected to implement MES.
MES defined
MES is an acronym that standsfor Manufacturing Execution Systems. Manufacturing Execution Systems derive their name from their inherent purpose of providing intelligent process control through an electronic system designed to execute instructions to control manufacturing operations. A collaborative manufacturing framework intrinsically aligns a company's manufacturing IT infrastructure with its business strategy. It allows the participants to map existing conditions and establish migration paths for improvements. Users also identify new ways of leveraging web-based technologies and working with strategic partners to compete more effectively.
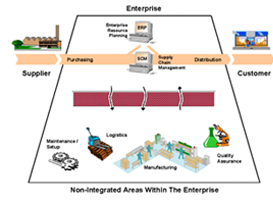
The ISA-95 standard separates the enterprise application functionality into three identifiable layers. The top layer is referred to as Business Planning and Logistics, which handles the supplier and customer-facing applications and the internal business level functions related to resource planning, product life cycle management, financials, inventory management and logistics. |
 |
The bottom layer of functionality applies to the specific process control activities related to batch, continuous and discrete control. This is the layer of control that is responsible for the physical control of the machinery and manual processes used for manufacturing.
Manufacturing operation management is the middle ground between the two other functional layers and is the modern equivalent of MES. This standard provides a clear picture of the various functional activities and high-level information flows found within manufacturing operations management in enough detail to define and implement MES solutions.
MES delivers the benefits
Quality and compliance are deriving the companies to focus on regulatory reporting, maintaining specifications, as well as visualizing into the quality process. This is being accomplished with MES.
Small and midsize manufacturers are conducting business on a global scale and using MES technology to get the job done. The changing demand patterns of customers are driving manufacturers to take a deeper look at how they can quickly meet those needs to be able to continue to compete on a global basis, which for many has meant investing in MES (manufacturing execution system) solutions. To the extent that manufacturing execution systems manage processes designed to achieve specific business objectives, an efficient MES can ideally exist within a Collaborative Manufacturing environment. This is a framework for organizing and controlling the key business processes of a manufacturing enterprise. A good MES addresses this at a fundamental level. Another area typically covered by
MES relates to the handling of Overall Equipment Efficiency (OEE) and Overall Plant Efficiency (OPE).
Some of the benefits are:
- Better monitoring and control of the entire manufacturing operations inclusive of maintenance, quality and inventory movements
- Agility in the manufacturing plant floor, resulting in agility across the enterprise
- Better co-ordination and information flow between planning & scheduling, production, quality control and material management processes
- Shorter lead time from order-to-delivery cycle
- Increased output
- Reduced production costs, better quality, improved regulatory compliances, environmental health and safety aspects
- Better visibility and control of the manufacturing supply chain
MES trends in Indian market
In one of the survey that was conducted in the first quarter to FY 07 across top 5,000 companies the results did show that local market is aware about the benefits, but little reluctant when it comes to adopting. |
|
|
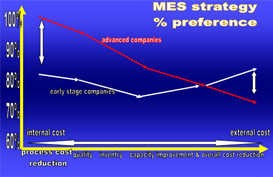
Trends 1: How do companies see the benefits of MES strategy?
The best in class companies clearly know the benefits of an MES as seen the MES strategy graph. The companies that are still at an early stage are unsure of the benefits. These are mangers who still deal with day to day crisis. They can not see the strategic benefits.
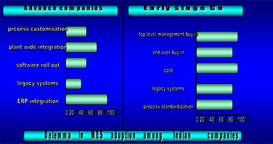
Trend 2: Key dilemma in MES adoption
The companies with multiple production disciplines: design and configure, production management, data management, quality compliance, asset management, and performance and visibility have entirely different challenge in the adoption of MES. Integrating a plant wide architecture with enterprise still remains the toughest challenge. For traditional company still stuck with work flow processes and using legacy systems the problems are very typical to Indian scenario. The cost, management buy in, user’s buy-ins etc. Despite this some of the smaller players have taken lead in MES adoption.
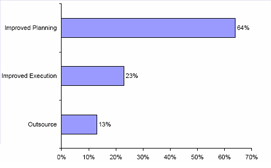
Trend 3: Overall measurable workflow improvement
The best in class companies reported overall improvement in their work flow processes. Almost sixty four per cent reported improvement in their production planning and scheduling. Twenty three per cent felt improvement in execution process. Almost thirteen per cent could optimise their out sourcing process. |
 |
Steps for MES success
Business leaders are faced with many hard decisions. Strategic planning and technology
Assessments often overlaps A collaborative manufacturing framework intrinsically aligns a company's manufacturing IT infrastructure with its business strategy. It allows the participants to map existing conditions and establish migration paths for improvements. Users also identify new ways of leveraging web-based technologies and working with strategic partners to compete more effectively. The result is a common perspective for the selection and integration of technologies among manufacturing operations, IT, business planning, plant systems, and other areas. A solid manufacturing execution system must not only meet specific process control requirements, but it must also coexist harmoniously with the rest of the production environment. Reliability, adaptability, cost-effectiveness and multiple-interface capabilities are all essential to achieving the desired business objective(s).
This is only the executive summary of the Research Report. For further information on this research report please write to us at info@texasventures.us
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|